PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
222-211-9
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
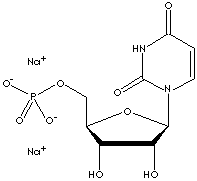
Urasil is a pyrimidine base, occurring condensed with ribose or deoxyribose to form the nucleosides uridine and deoxyuridine in animal cells. It is a fundamental unit or base of nucleic acids. When N1 is linked to the C1 of ribose, urasil forms a pyrimidine nucleoside called uridines which are phosphorylated with from one to three phosphoric acid groups to form the three nucleotides; uridine monophosphate (UMP), uridine diphosphate (UDP), and uridine triphosphate (UTP) respectively. When N1 is linked to the C1 of deoxyribose, deoxy nucleosides and nucleotides are formed from urasil and deoxyribose; deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP), deoxyuridine diphosphate (dUDP), and deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP). UTP is an activated precursor in the synthesis of UDP-linked hexoses. UDP acts as the chief transferring coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism to produce sucrose in plants, lactose and glycogen in mammals, and chitin in insects. UTP is involved in the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as a donator of phosphate groups to adenosine diphosphate (ADP). Uridine is important in biosynthesis of DNA and in the preservation and transfer of genetic information. It is known that there is no uridine in ribonucleic acid (RNA); the uridine nucleotides contain only deoxyribose.
- Urasil: a pyrimidine base
- Uridinea pyrimidine nucleoside
- Uridine Monophosphate (UMP, Uridylic acid): a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of uridine; a component of ribonucleic acid.
- Uridine Diphosphate (UDP): a nucleotide, the 5'-pyrophosphate of uridine; acting as the chief transferring coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism; acting as a carrier of hexoses, hexosamines, and hexuronic acids which are intermediates in the metabolism.
- Uridine Triphosphate (UTP): a nucleotide, the 5'-triphosphate of uridine; acting as a precursor in the synthesis of ribonucleic acid and of UDP-linked intermediates.
- Deoxyuridine Monophosphate (dUMP): a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of deoxyuridine; an intermediate in the synthesis of deoxythymidine triphosphate. (deoxy-, also called desoxy, is a prefix for the designation of compounds which contain one less atom of oxygen than the reference substance).
- Deoxyuridine Diphosphate (dUDP): a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of deoxyuridine; an intermediate in the synthesis of deoxythymidine triphosphate.
- Deoxyuridine Triphosphate (dUTP): a nucleotide, the 5'-triphosphate of deoxyuridine; an intermediate in the synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides.
Chemically modified nucleotides substituted or attached by special chemical groups or elements are studied and used to inactivate the normal biological operation in the living organism and the function of important enzymes.
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
WATER
15.0% max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
Price: